Food Safety and Quality
(GRI 416-1; 417-1; 417-3; FP7; FP8)
Food safety and quality are at the heart of our business. We continually review every aspect of our daily operations to make sure we provide safe, high-quality, nutritious products for our customers and consumers.
It starts with the health and well-being of the live animal. No matter the production system deployed, the health and welfare of our animals remains our priority, and we are committed to providing proper care to our animals. Please visit Our Animals and Our Supplier Partners for additional information on this topic.
Within our processing operations, we have a robust global food safety and quality program that consists of Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs), Sanitation Standard Operating Procedures (SSOPs), Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) procedures, and validated technology interventions that are designed to eliminate or reduce biological, chemical, and physical hazards from raw material production.
Each of these processes are monitored by JBS team members trained in food safety and quality assurance, as well as government officials, in each production facility. Additionally, inspection and process verification by government officials occur before the mark of inspection can be placed on products entering into commerce.

Our Regional Approaches:
Australia:
In Australian beef, smallstock, and pork processing facilities, the Department of Agriculture, Fisheries, and Forestry (DAFF) representatives are permanently located at our export facilities...
Australia:
In Australian beef, smallstock, and pork processing facilities, the Department of Agriculture, Fisheries, and Forestry (DAFF) representatives are permanently located at our export facilities and perform inspections of our facilities daily to ensure that we are meeting all federal food safety and overseas markets requirements.
Huon’s fish processing facilities are audited twice annually to ensure compliance to export and federal food safety requirements.
In New Zealand, the Ministry for Primary Industries (MPI) audits against food safety, and biosecurity standards on a risk-based frequency.
Brazil:
In Brazil, our production plants and products are inspected by the Ministry of Agriculture and Livestock (MAPA) and/or by the Brazilian Health Regulatory Agency (ANVISA).
Canada:
In Canada, the Canadian Food Inspection Agency (CFIA) regularly inspects and actively monitors our facilities to ensure compliance with federal food safety standards.
Europe:
In Europe and the U.K., our production facilities are inspected and third-party audited according to the European Union Food Hygiene and...
Europe:
In Europe and the U.K., our production facilities are inspected and third-party audited according to the European Union Food Hygiene and Food Standards Agency regulations, respectively, and any additional customer quality requirements to verify compliance.
Mexico:
In Mexico, we follow the best practice guidelines for chicken production as defined by the Secretariat of Agriculture, Livestock, Rural Development, Fisheries and Food (SAGARPA) and the...
Mexico:
In Mexico, we follow the best practice guidelines for chicken production as defined by the Secretariat of Agriculture, Livestock, Rural Development, Fisheries and Food (SAGARPA) and the National Service for Agro-Alimentary Public Health, Safety and Quality (SENASICA). Additionally, most Pilgrim’s facilities in Mexico have a Federally Inspected Type (TIF) certification.
United States:
In the U.S., the U.S. Department of Agriculture’s (USDA) Food Safety and Inspection Service (FSIS) inspect each of our animal protein production facilities daily to ensure that our food products meet federal food safety standards.
All JBS business units also have a written Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) program and a recall/market withdrawal procedure that provides for traceback and trace-forward capabilities to ensure proper product identification, if necessary. New JBS team members in relevant roles receive training on quality assurance and food safety management systems when they are hired and additional job-specific training as necessary. In addition, JBS Global Food Safety and Quality Assurance (FSQA) team members are provided with specific HACCP, as well as additional food safety and quality assurance training every year.
Led by the Global Head of Food Safety and Quality Assurance, our FSQA team is structured to ensure strong performance and corporate oversight at the highest level. Based in the U.S., our Global FSQA Department is responsible for establishing overarching guidelines, metrics, and priorities that are then deployed locally at each business unit by specialized teams. This streamlined reporting structure demonstrates the high priority we place on food safety and quality assurance and allows us to quickly and efficiently implement action-oriented decisions on a daily basis, if necessary.
Local best practices are also shared companywide during quarterly meetings hosted by the Global FSQA Department. This regular correspondence allows our team members to discuss successful past experiences, current initiatives, and future projects, and set targets to make sure we deliver results.
Finally, as part of our research and innovation efforts, we have microbiological testing and biotechnology laboratories in our operations around the world. Using state-of-the-art infrastructure and equipment, we are able to track various food safety metrics across our different brands and receive increasingly accurate testing results in less time.
Training and Audits

New JBS team members in relevant roles receive training on quality assurance and food safety management systems when they are hired and additional job-specific training as necessary. In addition, FSQA team members are provided with specific HACCP, as well as additional food safety and quality assurance training every year.
Each year, we conduct numerous food safety and quality system audits using accredited, independent auditing firms. In 2023, 73.3% of our global facilities were audited and certified by audit schemes recognized by the GFSI, one of the most stringent food safety-related audits available to the food industry. This represented a 5.9% increase from our percentage of certified facilities in 2022.
| GFSI Certified Plants by Region (GRI 416-1) | |
| Global | 80% |
| Australia | 91% |
| Brazil | 58% |
| Canada | 100% |
| Europe | 100% |
| Mexico | 63% |
| United States | 100% |
| Percent of Significant Product Categories Assessed for Health and Safety Impact Improvements (GRI 416-1) | |
| Global | 83% |
| Australia | 52% |
| Brazil | 100% |
| Canada | NC |
| Europe | 100% |
| Mexico | 100% |
| United States | NC |
Internal audits and inspections are also conducted by our FSQA team members. In 2023, we completed a third year of collecting and compiling data against our internal Global Food Safety and Quality Assurance Scorecard, which was developed to benchmark performance indicators across global operations and business units, bolster accomplishments by identifying areas of improvement, and encourage the pursuit of continuous and positive results. To determine the scorecard’s indicators, our Global FSQA team reviewed relevant standards, requirements, and metrics. Now, it evaluates 11 metrics across four priority pillars, including regulatory compliance, animal welfare and prevention of antimicrobial resistance, customer and consumer satisfaction, and product safety and quality. For instances where there is a product recall to protect public health, we have standardized operating procedures that outline each step of the process to ensure all affected products are promptly tracked and removed from distribution channels. To inform our customers and consumers of a recall, we issue a notice that follows local government guidelines for communication.
(SASB FB-MP-250a.1)In the Event of a Recall
Even though we have comprehensive systems in place to provide our consumers with safe, high-quality foods, instances can and have occurred where a product recall is necessary to protect public health. In these cases, we have standardized documents that outline each step of the process to ensure all affected products are promptly tracked and removed from distribution channels. To inform our customers and consumers of a recall, we issue a notice that follows local government guidelines for communication.
- In the U.S., recall information is also posted on the USDA FSIS or FDA websites.
- In Australia and New Zealand, recall information is communicated on the Food Standards Australia New Zealand (FSANZ) website.
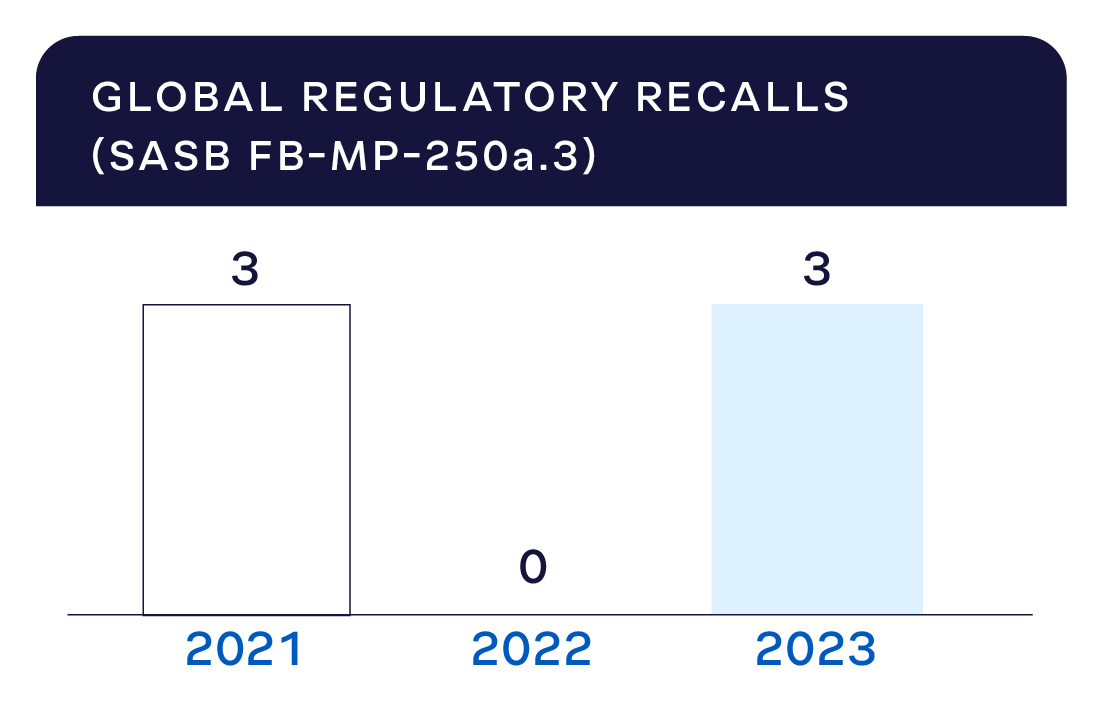
In 2023, there were three regulatory recalls due to food safety or quality in our global operations.
Recalls are rare, and we work diligently to understand how they were caused and how to prevent future incidents. We perform comprehensive root-cause analyses and share our learnings across JBS. As an independent third-party auditor, the GFSI verifies the effectiveness of our corrective actions.
Case Studies:
- Building strong relationships among FSQA leaders;
- Collaborating and learning about KPIs to set global ESG goals;
- Fostering new learnings while stimulating the exchange of ideas through tours of production facilities;
- Educating on best-in-class technologies;
- Learning from external presenters, triggering an exchange of experiences on the food safety culture, animal welfare, and innovation concepts; and
- Returning home with key takeaways to be applied in their operations.

