Our Environment
Energy Management
(GRI 3-3)

Around the world, JBS operations are dedicated to improving on-site energy efficiency and increasing the use of both direct and indirect energy from renewable sources.
As a material topic for our business, both in terms of its impact on our GHG footprint and general eco-efficiency, energy management is addressed globally through a four-pronged strategy, focused on:
• Identifying opportunities
by sharing best practices between company facilities, measuring and monitoring performance, and conducting energy-focused site audits
• Implementing behavioral improvements
by establishing energy key performance indicators (KPIs) for each JBS facility, which prompt the implementation of no- or low-cost methods of reducing emissions through behavior
• Approving capital expenditure upgrades
through capital investments to upgrade non-energy-efficient equipment, capture and use waste heat, and eliminate other inefficient processes
• Using renewable energy
by procuring both onsite and/or virtual renewable energy sources for the areas where physical decarbonization of company assets is not feasible.
We apply this strategy against all sources of energy consumption and support it through our environmental data management systems at both business-unit and facility levels. In addition to total energy use and total renewable energy use, one of the key metrics we monitor is energy intensity (total energy use per unit of production).

Energy Efficiency
To reduce energy use in our facilities, our environmental and engineering teams are dedicated to identifying operational efficiencies, replacing equipment, and leading behavioral improvements by example. Alignment to internal processes allows us to recognize and prioritize impactful projects that ranged across a variety of areas and topics, such as optimization of refrigeration and steam operations, conversion to LED lighting, improvement of fleet fuel efficiency in our transportation units, covering of anaerobic wastewater lagoons for biogas collection, and more.
Our efforts to identify and execute energy improvements are evidenced through our financial commitment. Thousands of projects are implemented annually to improve production, food safety, and mechanics, among a variety of other reasons, but in each project our teams incorporate energy efficiency, which often results in incremental capital spend.
Since 2021, we have invested more than US$ 150 million across hundreds of projects inside our own facilities to reduce scope 1 and 2 emissions, primarily tied to energy use and methane destruction. Collectively, these initiatives will represent an annual reduction of over 400,000 metric tons of CO2e.
Renewable Energy
In tandem, we are investing globally to increase our proportion of total energy consumption from clean sources. Globally, 36% of our energy use and 8% of our electricity use were derived from renewable sources in 2023. In accordance with GHG reporting protocols, we report both market-based and location-based scope 2 emissions and renewable electricity (RE) purchases. RE is dominant on Brazil’s national electricity grid, however we have refined our reported RE percentage as per updated emission factors and protocols. While this conservative approach has significantly reduced our historically reported RE purchases, it has not materially affected our reported scope 2 emissions.
Global Energy Consumption¹(GRI 302-1; 302-3; 302-4) |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | |
| Energy Use (MWh) | 25,582,089 | 21,209,776 | 21,937,268 | 20,752,370 | 21,968,507 |
| Energy Use Intensity (MWh/MT of finished product produced) | 1.26 | 1.05 | 1.02 | 0.96 | 0.99 |
| Renewable Energy Use (%) | 25% | 30% | 31% | 33% | 36% |
| Non-Renewable Energy Use (%) | 75% | 70% | 69% | 67% | 64% |
Global Scope 1 Energy Consumption²(GRI 302-1; 302-3; 302-4) |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | |
| Scope 1 Energy Use (MWh) | 19,097,746 | 14,364,025 | 15,210,827 | 14,860,717 | 15,904,822 |
| Scope 1 Energy Use Intensity (MWh/MT of finished product produced) | 0.94 | 0.71 | 0.71 | 0.69 | 0.72 |
| Renewable Energy Use (%) | 33% | 43% | 42% | 43% | 46% |
| Non-Renewable Energy Use (%) | 67% | 57% | 58% | 57% | 54% |
Global Scope 2 Energy Consumption³(GRI 302-1; 302-3; 302-4) |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | |
| Scope 2 Energy Use (MWh) | 6,484,343 | 6,845,751 | 6,726,441 | 5,891,653 | 6,063,684 |
| Scope 2 Energy Use Intensity (MWh/MT of finished product produced) | 0.32 | 0.34 | 0.31 | 0.27 | 0.27 |
| Renewable Electricity Use (%) | 2% | 4% | 5% | 8% | 8% |
| Non-Renewable Electricity Use (%) | 98% | 96% | 95% | 92% | 92% |
2 Includes direct energy consumption [electricity generated on-site, the use of fuel to generate steam and heat (stationary combustion) and consumption of fuel by company-owned vehicle fleets (mobile combustion)].
3 Includes indirect energy consumption [purchased electricity, steam, heat, and cooling].
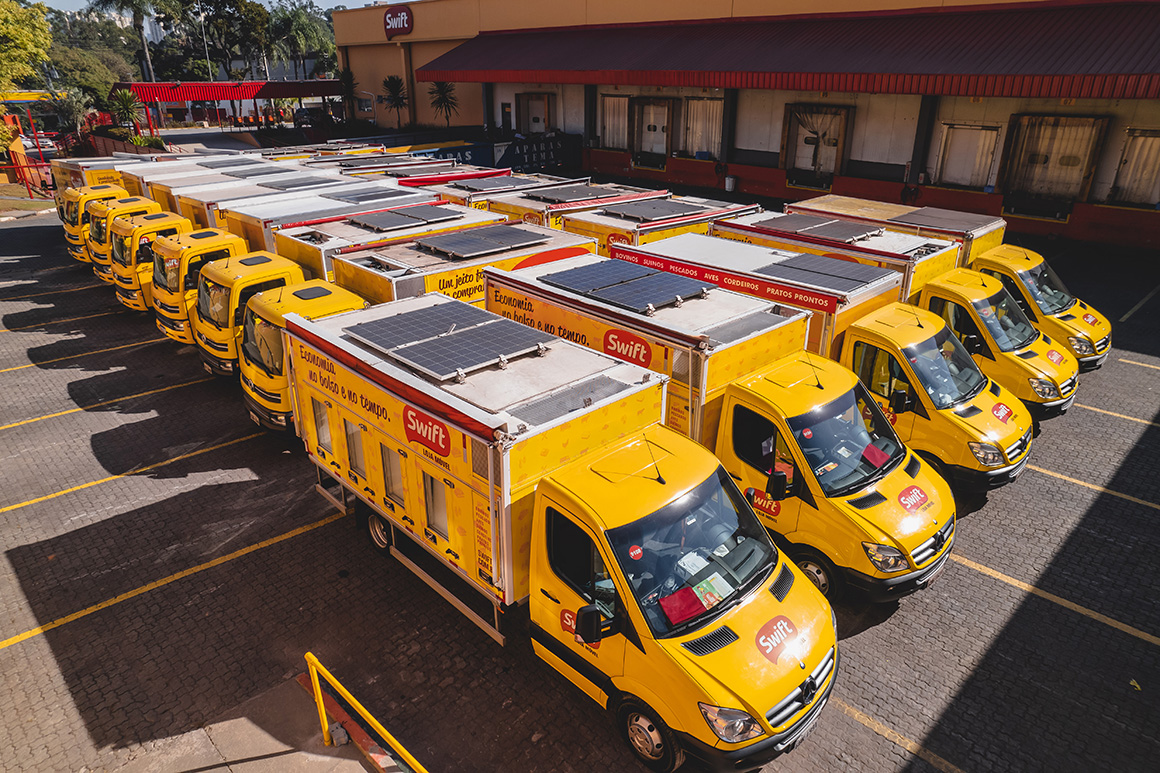
Case Studies:
As solar power continues to become a more available source of renewable electricity, we believe it can help us reach our global goal of net-zero GHG emissions and meet the energy demands of our facilities.
Energy-related key performance indicators (KPIs) were also closely evaluated through regular performance reviews, and improved metering system deployment and analysis were advanced. Finally, sharing utility reduction activities and improvements between facilities was also found to be effective.
