Our Environment
Water and Wastewater Management
(GRI 3-3; 303-1; 303-2; SASB FB-MP-140a.2)
Water stewardship is crucial to the resilience of our global community and business. Water is a critical component in the production of safe, high-quality food. The decreasing availability of clean, accessible water threatens food security around the world. According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations, agriculture represents 70% of all freshwater withdrawals, and as one of the largest global food companies, we recognize we must play a fundamental role in helping protect the responsible use of this critical resource.
In 2023, we invested US$ 27 million in Operational efficiency related to water.

Water Use
Within our operations, we embrace our responsibility to decrease water use by monitoring withdrawal and usage and prioritizing reductions at every facility, while still preserving our high standards for food safety and sanitary conditions. Our Global Water Stewardship Policy guides our businesses, encouraging the development of strategies and projects that minimize the need for new water sources.
Each facility sets water-use goals and targets to encourage ownership and accountability and devotes financial resources to maintain alignment with business-specific policies and commitments. We also work cross-functionally with our environmental, engineering, operations and food quality and safety teams when designing and implementing conservation strategies to ensure they do not interfere with water quality of food safety protocols.
The primary indicators we measure related to water use include total water withdrawal by source, total water reused, and total water use intensity (water use per unit of production) to consistently identify opportunities for improvements, irrespective of changes in production. Unfortunately, we increased our water use 4% from 2019 to 2023. However, we will continue to focus on water in 2024 and beyond, ensuring that we stay committed to reducing usage of this critical resource while maintaining our high team member and food safety standards.
Global Water Withdrawal by Source (m³)(GRI 303-3; 303-5) |
||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023* | ||||||
| Surface | 45,228,057 | 26.30% | 44,748,043 | 26.15% | 45,997,592 | 25.44% | 72,053,277 | 42.08% | 106,366,267 | 42.22% |
| Groundwater | 57,677,295 | 33.50% | 56,957,299 | 33.28% | 60,148,519 | 33.27% | 63,577,839 | 26.35% | 70,121,232 | 27.83% |
| Municipality | 68,940,053 | 40.09% | 69,323,367 | 40.51% | 74,643,945 | 41.29% | 76,188,320 | 31.57% | 75,454,473 | 29.95% |
| Other | 115,805 | 0.07% | 113,939 | 0.07% | 0 | 0.00% | 0 | 0.00% | 0 | 0.00% |
Wastewater
Management
We monitor the treatment of all wastewater produced in our operations in accordance with appropriate regulatory standards. All processing facilities have wastewater treatment programs specifically tailored to their unique discharge permit requirements to help reduce our total discharged water volume and address noncompliance issues.
Depending on the operation, wastewater is either fully treated at our facilities or pre-treated on-site then fully treated in the municipal system.
Global Water Discharge by Recipient (m³)(GRI 303-4) |
||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | ||||||
| Water Body | 80,931,603 | 52.62% | 80,361,473 | 55.52% | 83,400,523 | 56.84% | 139,238,188 | 70.95% | 148,073,190 | 71.82% |
| Municipality | 47,130,042 | 30.64% | 50,134,143 | 34.64% | 50,447,505 | 34.38% | 49,680,658 | 25.32% | 50,280,615 | 24.39% |
| Land Application | 18,349,248 | 11.93% | 13,983,917 | 9.66% | 12,886,170 | 8.78% | 7,208,364 | 3.67% | 7,708,050 | 3.74% |
| Other | 7,406,135 | 4.81% | 262,056 | 0.18% | 6,557 | 0.00% | 109,911 | 0.06% | 124,309 | 0.06% |
Global Water Consumption* (m³)(GRI 303-5) |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | |
| Total Water Consumption | 18,144,182 | 26,401,059 | 34,049,301 | 45,964,890 | 46,992,919 |
Water
Impact
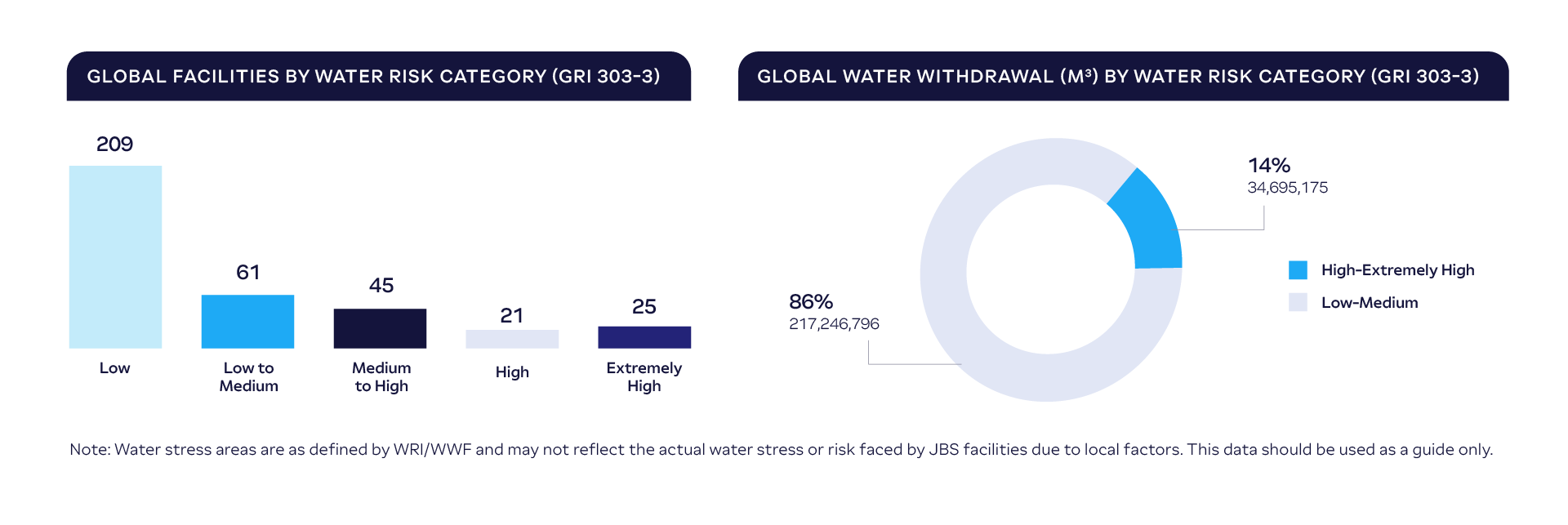
Conducting water risk assessments is also a critical element of our strategy and allow us to better identify and prioritize water resource projects that are locally relevant to each watershed and reduce the company’s overall water impact. We conduct assessments of our operations based on the World Resources Institute (WRI) Aqueduct and World Wildlife Fund (WWF) Water Risk Filter. This process allow us to identify areas with high, medium and low exposure to water-related risks, including quantity (baseline water stress, inter-annual variability, seasonal variability, flood occurrence, drought severity, upstream storage and groundwater storage), quality (return flow ratio and upstream protected land), and regulatory and reputational risk (media coverage, access to water and threatened amphibians).
In 2023, we invested US$ 16.9 million on purchasing water due to water stress.
2023 Percent of Facilities Located in Water Stress Areas(GRI 303-3) |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low | Low to Medium | Medium to High | High | Extremely High | |
| Australia | 34% | 0% | 12% | 29% | 24% |
| Brazil | 86% | 3% | 8% | 3% | 0% |
| Canada | 0% | 50% | 0% | 50% | 0% |
| Europe | 21% | 75% | 1% | 3% | 1% |
| Mexico | 14% | 11% | 3% | 5% | 68% |
| United States | 53% | 8% | 19% | 6% | 13% |