Management and Oversight
(GRI 2-9)
Governance Structure
Effective governance is essential to achieving sustainable business practices and creating long-term value for all stakeholders. Our corporate governance goes beyond compliance with all laws and regulations by adhering to our internal policies and commitments.
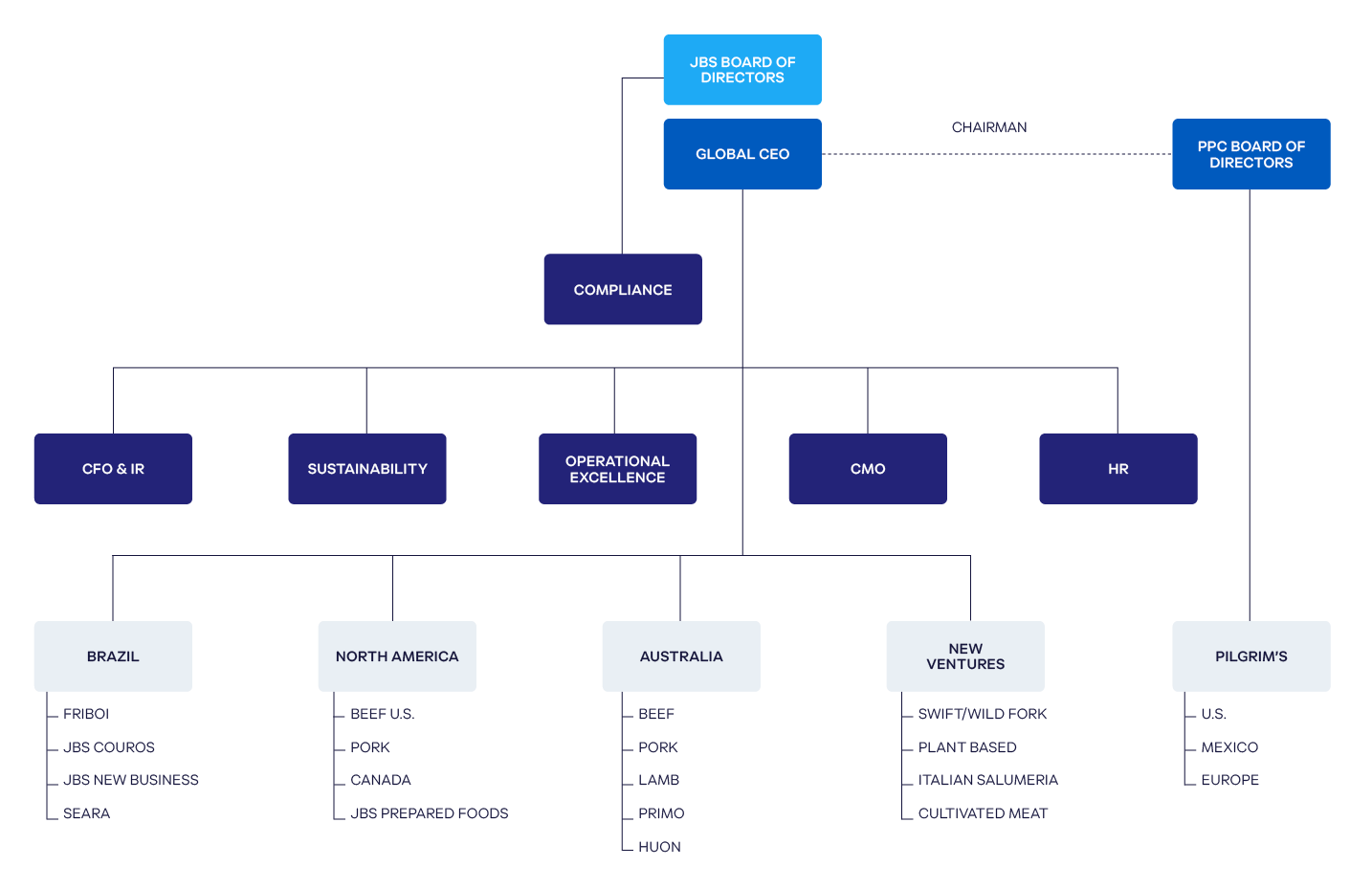
Board of Directors
(GRI 2-12, 2-13, 2-17)
Our Board of Directors is our highest governance body. It comprises 11 members, including a chair, a deputy chair and nine independent directors, including two women. Elected at general shareholders’ meetings for renewable terms of two years, members determine business guidelines and policies and economic, environmental, and social targets for JBS. They are also responsible for monitoring the company’s performance and overseeing the management of the Board of Executive Officers.
Each board member provides unique expertise and geographic perspective. Comprised chiefly of independent members, the board helps ensure that credible, expert, and objective voices help guide the direction of our business.
Board Advisory Committees
(GRI 2-9)
The JBS Board of Directors is supported by six specific committees that assist in strategic business decisions.
- Socio-Environmental Responsibility Committee
Advises the Board of Directors on sustainability risks and opportunities. The committee is responsible for addressing all topics related to the company’s business from a global sustainability perspective, including identifying critical issues that impact the business; monitoring and implementing initiatives, policies, and strategies; and evaluating investment proposals related to sustainability.
- Statutory Audit Committee
Advises the Board of Directors regarding the norms, rules, and procedures for disclosure and transparency of financial statements. The committee also reviews the work conducted by the internal audit team and external audits, evaluates the performance of internal control systems, and approves the guidelines and action plans for the year.
- Financial and Risk Management Committee
Helps the Board of Directors and Executive Officers analyze the financial impacts of potential global economic scenarios on the JBS business. The committee improves rules and procedures for controlling and managing market and credit risks to reduce the risk of price fluctuation, mitigate other relevant risks, and ensure shareholder value.
- Governance, Compensation and Nomination Committee
Implements practices and policies based on high corporate governance and compliance standards.
- Related Parties Committee
Ensures that transactions between related parties and the company, its subsidiaries, and its affiliates are performed in the best interests of the company and fair to all involved. The committee negotiates independently under normal market conditions through a transparent and ethical process in accordance with current legislation and on terms not less favorable to the company than a transaction held with third parties not considered related parties.
- Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion Committee
Advises the Board of Directors on the company’s progress related to people management (recruitment, hiring, training, promotion, and resignation) through the definition, implementation, and management of diversity and inclusion programs. The programs promote an inclusive and diverse workplace aligned with the company’s strategy, culture, and values. The committee develops affirmative actions based on an evaluation of the company’s programs and employee feedback.
To learn more about JBS’ Board of Directors, please visit our Investor Relations site.
Board of Executive Officers
The JBS Board of Executive Officers is its managing executive body. Executive officers are the company’s legal representatives, responsible for JBS’s internal organization, decision making, daily operations, and the implementation of general policies and guidelines periodically established by the Board of Directors. The executive board also oversees the execution of the company’s sustainability strategy across its global operations.
Risk Management
JBS has a global risk management team that operates under its own Risk Control Board, which has direct access to the company’s senior management through the Financial and Risk Management Committee that advises the Board of Directors. This team was created to track the factors and variables that could expose the company to financial issues such as market, credit, and liquidity risks, and non-financial issues such as socioenvironmental matters like climate change.
The Risk Control Board detects, monitors, assesses, and mitigates financial risks inherent to the company’s operations. Based on the Commodities and Financial Risk Management Policy approved by the Board of Directors, the Risk Control Board also assists operational units in identifying and monitoring the risks posed by their activities, with assistance from expert professionals and dedicated systems.
Within our subsidiaries, the Pilgrim’s ESG Committee assists the Pilgrim’s Board of Directors in overseeing the company’s environmental, social, and governance policies, strategies, and programs. These include climate change impact, energy conservation, human rights, diversity and inclusion, and employee health, safety, and well-being. Through its oversight role, the committee helps ensure that Pilgrim’s executive officers and other senior managers design, fund, implement, and execute programs consistent with the company’s ESG objectives.
Category |
Risk |
Description |
Responding to the Risk |
| Cyber | Cybersecurity | Unprotected or exposed information assets (such as hardware, systems, laptops, customer data, and/ or intellectual property) that may be vulnerable to a cyber attack, leading to financial impacts, operational disruptions or downtime, and damage to brands and reputations. |
|
| Operational | Animal Health | The occurrence of an animal disease outbreak in the country or a specific region can lead to a potential closure of significant markets and an increase in customer complaints. This outbreak may result in the inability to supply products and maintain operations in the factories. |
|
| Workforce Safety | Potential for occupational accidents or fatalities to occur if the company does not establish and/or provide a working environment where the safety of its employees is the top priority. | JBS has a Corporate Health and Safety practice dedicated to health and safety standards and processes. Each unit has a matrix organizational structure and OHS teams in each Operating Unit. In Brazil, risk management is carried out through the Self-management Health and Safety Program - PSSAG, which is integrated with legal requisites to contribute to the management of risksand hazards, where all tools have periodical updating and monitoring routines. There are Safety Committees operating from senior management down to the structure of each Operating Unit, which address specific topics and monitor the implementation of health and safety routines and processes, as well as departmental key performance indicators. | |
| Financial | Market | Exchange, interest and commodities risks, where fluctuations could potentially affect JBS’ operations |
|
| Credit | Risk of delinquency posed by accounts receivable, investment and hedging instruments | Accounts receivable from customers: Diversification of the portfolio and establishment of secure parameters for credit granting (always considering proportional limits, financial and operational ratios, and conducting credit monitoring agency inquiries). Financial transactions with financial institutions as counterparties: Exposure limits defined by the Risk Management Committee and approved by the Board of Directors, based on risk ratings from specialized international agencies. | |
| Liquidity | The possibility of imbalances between tradable assets and payable liabilities that could affect the ability to meet upcoming financial obligations. | Capital structure management focused on modified immediate liquidity metrics – that is, cash and cash equivalents plus financial investments, divided by short-term debt – and working capital, to maintain the leverage of the Company and its subsidiaries. In 2019, a Liquidity Management Policy was published, establishing guidelines for the liquidity management process of the Company and its subsidiaries, both in Brazil and abroad. | |
| Social and Environmental | Acquisiton of Raw Materials | The risk of acquiring raw materials from suppliers involved in deforestation of native forests, encroachment on protected areas such as indigenous lands, quilombolas, local communities, or environmental conservation units, as well as the risk of utilizing child labor or forced labor, or products that may pose health risks to consumers. |
|
| Climate Change | Climate change could also negatively impact the company’s business. Resources such as water, electricity and animal feed (dependent on farming) are essential for producing raw materials (cattle, poultry, hogs and sheep). Operations could also be impacted by new legislation and regulations around the matter. |
|
|
| Compliance | Corruption | Risk of conduct contravening JBS’ Code of Conduct |
JBS has a global compliance program that encompasses the following pillars:
|

