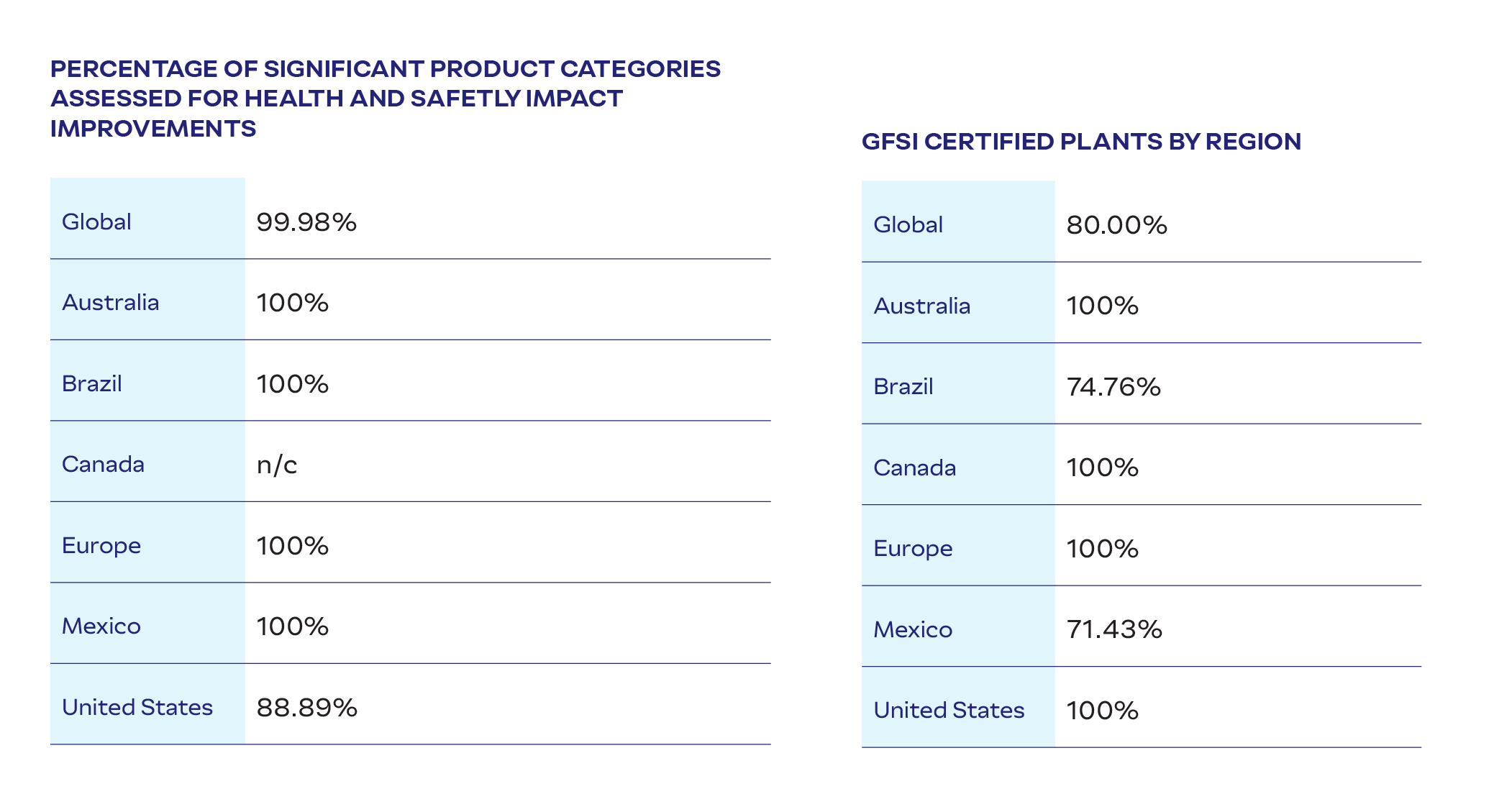
Health and Safety
(GRI 2-23, 3-3, 403-1, 403-2, 403-3, 403-4, 403-5, 403-6, 403-7, 403-8, 403-9
SASB FB-MP-320a.1, FB-MP-320a.2)

The health and safety of our team members is paramount. Across all regions, we integrate health and safety into our organizational fabric, tailoring strategies to local contexts while maintaining global standards. Our Global Health and Safety Policy serves as the foundation for our strategy and management approach, promoting alignment with relevant regulatory requirements in every country where we operate. We also have established formal global health and safety committees, with representation from both management and hourly workers.
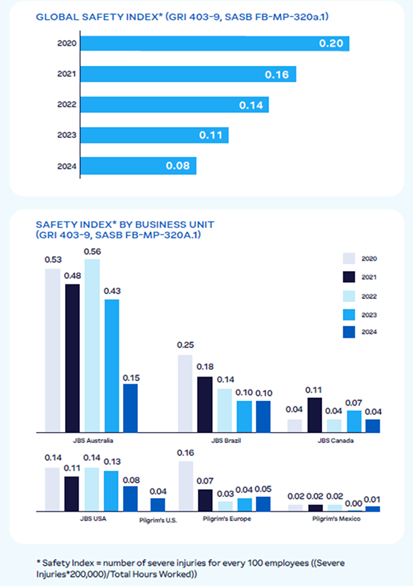
Throughout our operations, we work to foster a culture of accountability that empowers each team member to understand and practice health and safety guidelines while remaining vigilant. This is reinforced by frequent team member training and development around our Global Health and Safety Policy and Code of Conduct and Ethics. In addition, we regularly evaluate the effectiveness of our programs by conducting internal and third-party audits, collecting feedback, and making any adjustments as needed. Globally, JBS has a goal to improve performance against its Global Safety Index* by 30% by 2025 vs. a 2019 baseline. As of 2024, we have achieved a 71% improvement.
*Safety Index = number of severe injuries for every 100 employees [(Severe Injuries*200,000)/Total Hours Worked]. Severe Injury = Any injury resulting in amputation, fatality, in-patient hospitalization, vision loss, second- or third-degree burns, or fractures that results in greater than fifteen days lost time, and any other injury that results in greater than fifteen days lost time.
Although independent contractors comprise a small portion of our total workforce, we protect the health and safety of our contractors similar to our approach to our employees.
JBS Global Health and Management System Coverage
(GRI 403-8)
| JBS Global Health and Management System Coverage | |||
| Workforce Type | Covered by a Health and Safety Management System | Covered by a Health and Safety Management System that is Internally Audited | Covered by a Health and Safety Management System that is Externally Audited or Certified |
| Employees | 100% | 93% | 15% |
Our safety governance structure and management approach are guided by our Global Workplace Health and Safety Policy and aligned to the relevant regulatory requirements of each country in which we operate. We defer to governing bodies like those listed below to evaluate the effectiveness of external safety audit processes, collect feedback, and make necessary adjustments.
Health and Safety Programs :
(GRI 403-1, 403-2, 403-3, 403-4, 403-7, 403-9, SASB FB-MP-320a.1)
Australia:
JBS Australia emphasizes safety through its Work Health and Safety Policy and Safety Framework, which conforms to...
Australia:
JBS Australia emphasizes safety through its Work Health and Safety Policy and Safety Framework, which conforms to the Australian Standard (AS) 4801, addressing risks such as contractor management, emergency response, and hazardous tasks. The Group Risk Team sets governance standards, while each division has safety operations managers and injury management resources supporting team members at the site level. Committees governed by legislation meet at least 10 times annually to review hazards, injuries, and safety program outcomes.
Brazil:
In Brazil, JBS operates under an Integrated Health and Safety Policy that supports...
Brazil:
In Brazil, JBS operates under an Integrated Health and Safety Policy that supports its Self-Management Health and Safety Program. This program standardizes procedures related to Occupational Health and Safety, monitoring compliance with legal and internal requirements while driving continuous improvement. Each business unit has dedicated health and safety leaders reporting to the Corporate Team, with site-level teams structured according to Regulatory Standard 4 (NR4).
Additionally, all units in Brazil have an Internal Commission for the Prevention of Accidents at Work (CIPA), which meets monthly to address process improvements and participate in inspections, risk mapping, and safety campaigns.
Canada:
In Canada, our Health and Safety Management System is aligned with the Alberta Occupational Health and Safety (OH&S) legislation. In addition, our Alberta facilites are a holder of...
Canada:
In Canada, our Health and Safety Management System is aligned with the Alberta Occupational Health and Safety (OH&S) legislation. In addition, our Alberta facilites are a holder of a Certificate of Recognition (COR) through certified auditor, Alberta Food Processing Association (AFPA). Through a 3rd part, the program confirms JBS Canada has a robust system in place to certify HSMS has been developed, implemented, and evaluated under Alberta Provincial Standards. The annual audit requirement encourages ongoing review and improvement of safety systems, making safety a proactive part of our operation. The program is overseen by the Safety and Health Services departments.
Europe:
Health and safety practices across Pilgrim’s Europe are guided by 10 Safety Principles and Health and Safety Executive RIDDOR (Reporting of Incidents, Diseases, and Dangerous Occurrences) regulations. Performance is driven by...
Europe:
Health and safety practices across Pilgrim’s Europe are guided by 10 Safety Principles and Health and Safety Executive RIDDOR (Reporting of Incidents, Diseases, and Dangerous Occurrences) regulations. Performance is driven by continuous improvement standards and measured against federal metrics, such as DART, and internal safety indexes. The Head of HSE & Risk leads a team of divisional and specialist resources to implement safety initiatives across the business, with additional facility teams reporting through divisional structures to maintain alignment with corporate strategy.
At Rigamonti, health and safety actions are conducted in accordance with applicable Italian and European legislation and guided by ISO 45001principles – to which four facilities are scheduled to receive third-party certification on in 2025. The program is overseen by a group HSE Manager as well as business-unit-specific health and safety representatives and occupational physicians.
Mexico:
Pilgrim’s Mexico promotes zero accidents and a culture of self-care and prevention among team members. Its health and safety structure includes...
Mexico:
Pilgrim’s Mexico promotes zero accidents and a culture of self-care and prevention among team members. Its health and safety structure includes national and corporate management teams, industrial safety headquarters, medical doctors, security technicians, and nurses, maintaining comprehensive oversight and alignment with company goals. Pilgrim’s Mexico also operates a Health and Safety Committee, which meets monthly to analyze workplace risks, incidents, and the effectiveness of safety measures, with authority to recommend safety policies.
United States:
In the United States, JBS follows the Occupational Safety and Health (OSH) Act of 1970, state, federal, and local regulations, and...
United States:
In the United States, JBS follows the Occupational Safety and Health (OSH) Act of 1970, state, federal, and local regulations, and Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) General Industry Safety Standards. Health and safety actions are overseen by a Shared Services Head of Safety, Health, Security, and Labor as well as the respective Heads of Safety for each business unit. Additional directors, managers, and facility-level personnel oversee the integration of safety practices into daily operations.
Further, most U.S. locations hold monthly safety committee meetings, while Pilgrim’s U.S. includes Department Safety Representatives (DSRs) who conduct pre-shift safety inspections and meet with Complex Safety Managers.
Actions to Support Health and Safety
(GRI 403-2, 403-3, 403-4, 403-7)
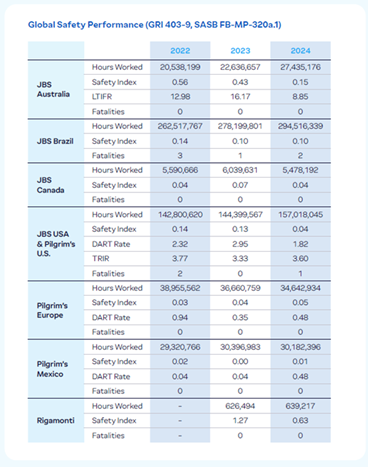
Global Safety Performace
(GRI 403-9, SASB FB-MP-320a.1)
Training and Education
GRI 403-5
We provide frequent health and safety training to minimize work-related injuries and illnesses across our facilities. This comprehensive training includes new team member orientation, job- and task-specific instruction, departmental safety meetings, and regular refresher courses. All newly hired team members are required to complete classroom and department-specific training, offered in multiple languages to promote accessibility.


Promoting Health and Well-being in the Workplace
GRI 403-6, SASB FB-MP320a.2
JBS is dedicated to supporting the health and well-being of our team members through comprehensive medical services, health promotion programs, and preventive care initiatives. Across our global operations, JBS provides access to both occupational and non-work-related health services, offering employees resources to maintain their physical and mental well-being.
In the U.S., many locations feature onsite Occupational Health Clinics staffed by licensed medical professionals, providing free care for work-related injuries and illnesses. JBS Australia promotes health and well-being through early intervention programs for work and non-work-related injuries, discounted private health insurance, and a Wellbeing App that provides remote access to counseling, diet, exercise, and financial support services. The company also organizes health checks, including skin and blood pressure screenings, to encourage preventive care. Pilgrim’s Mexico offers onsite infirmary services for immediate medical needs, regular health screenings, and vaccination campaigns.

