Our Environment
(GRI 2-5, 2-6, 3-3, 305-1, 305-2, 305-3, 305-4, 305-5)
(SASB FB-MP-110a.1, FB-MP-110a.2)
Our Climate Strategy
JBS has developed a climate strategy designed to build resilience throughout our value chain. Recognizing the importance of inclusivity and fairness, our approach is guided by a just-transition philosophy, supporting the transformation of food systems in a way that benefits both the environment and the people who sustain them. By fostering partnerships and prioritizing engagement, we work collaboratively with farmers, suppliers, and communities to advance sustainability while strengthening economic opportunities.
We strive to reduce the intensity of Scope 3 emissions through collaborative efforts that deliver both environmental and economic benefits for our supplier partners. Globally, we are investing in clean energy solutions, such as solar, wind, and biogas, to increase the share of renewable energy in our total consumption. Additionally, we are advancing climate resilience across our operations and value chains, enhancing the adaptability and productivity of food systems to withstand the changing climate, fortifying global food security while promoting sustainable practices across operations and supply chains.
Climate Goals and Ambition
We acknowledge that whether the company is successful in achieving this ambitious goal will depend on external factors outside of the company’s control, including but not limited to: national and local government leadership, the resources and efforts of those in our value chains, technological innovations, energy advancements, climate change impacts, collaborations and partnerships, and international agreements and global trends. See our Legal Disclaimer for further information.
With respect to our own operations and indirect energy, we set clear initial goals, including reducing Scope 1 and Scope 2 GHG emission intensity by 30%, compared to our 2019 baseline. These goals reflect our determination to lead progress in emissions reductions while driving innovation and collaboration across the global food system.
Climate Reporting and Assurance
For over a decade, we have measured, monitored, and reported direct and indirect GHG emissions, voluntarily disclosing data to the Carbon Disclosure Project (CDP), regional regulatory frameworks, and other platforms. Our GHG emissions are calculated using internationally recognized standards, including the World Resources Institute’s and the World Business Council for Sustainable Development’s The Greenhouse Gas Protocol: A Corporate Accounting and Reporting Standard (Revised Edition) (GHG Protocol), supplemented by internal criteria established by JBS.
To further strengthen stakeholder confidence, JBS has obtained third-party limited assurance for its global Scope 1 and Scope 2 GHG inventories from 2019 to 2024, and 2021 global Scope 3 inventory. In addition, JBS Brazil has undergone a reasonable assurance process for it’s Scope 1 and Scope 2 GHG emissions for the first time. Moving forward, we will continue to seek annual assurances for our emissions, reinforcing our dedication to accountability and continuous improvement.
In Brazil, JBS also participates annually in the Brazilian GHG Protocol Program, a nationally recognized platform that verifies emissions data and promotes transparency. This voluntary participation allows us to benchmark our progress against industry peers while showcasing our prioritization of sustainability leadership.
Driving Innovation Through Data Partnerships
JBS partners with industry leaders to develop innovative solutions for emissions measurement across the value chain. One such initiative is the CarbonPrime project, a proof-of-concept collaboration involving AMAGGI, Bayer, JBS, Rumo, and the Sumitomo Corporation of Americas. This groundbreaking effort integrates primary emissions data from agricultural operations, feed and food production, logistics, seed processing, trading, and distribution—from Brazil to global markets. By leveraging this detailed data, CarbonPrime delivers more accurate estimates of GHG emissions across the value chain, enabling actionable insights to accelerate decarbonization from seed to store.
In Australia, JBS’s Great Southern brand exemplifies its dedication to data transparency by completing the country’s largest carbon footprint assessment for grass-fed, grass-finished beef. Partnered with Integrity Ag, a leading consultancy specializing in agricultural sustainability, this initiative utilized data from the JBS Farm Assurance Program, which tracks sustainability practices at every stage of production, and integrated on-farm data with scientific methodologies to provide detailed insights into GHG emissions associated with cattle raised under the program.
Through partnerships like CarbonPrime, JBS continues to expand its capabilities in data collection and transparency, keeping our climate goals informed by robust and reliable information. These efforts not only enhance reporting accuracy but also empower stakeholders to collaborate on meaningful solutions to reduce emissions globally.
Sustainability Linked Bonds: Aligning Financial Mechanisms with Climate Goals
JBS leverages sustainability linked bonds as a financial mechanism to align our climate goals with measurable outcomes. These bonds are tied to specific sustainability performance targets for our goal to reduce Scope 1 and Scope 2 GHG emissions intensity by 30% by 2030.
Annual audits of our GHG inventories further strengthen compliance with emerging regulations, such as Brazil’s Emissions Trading System (SBCE), while confirming accuracy and reliability in our reporting. These efforts accentuate JBS’s proactive approach to environmental governance and climate accountability.
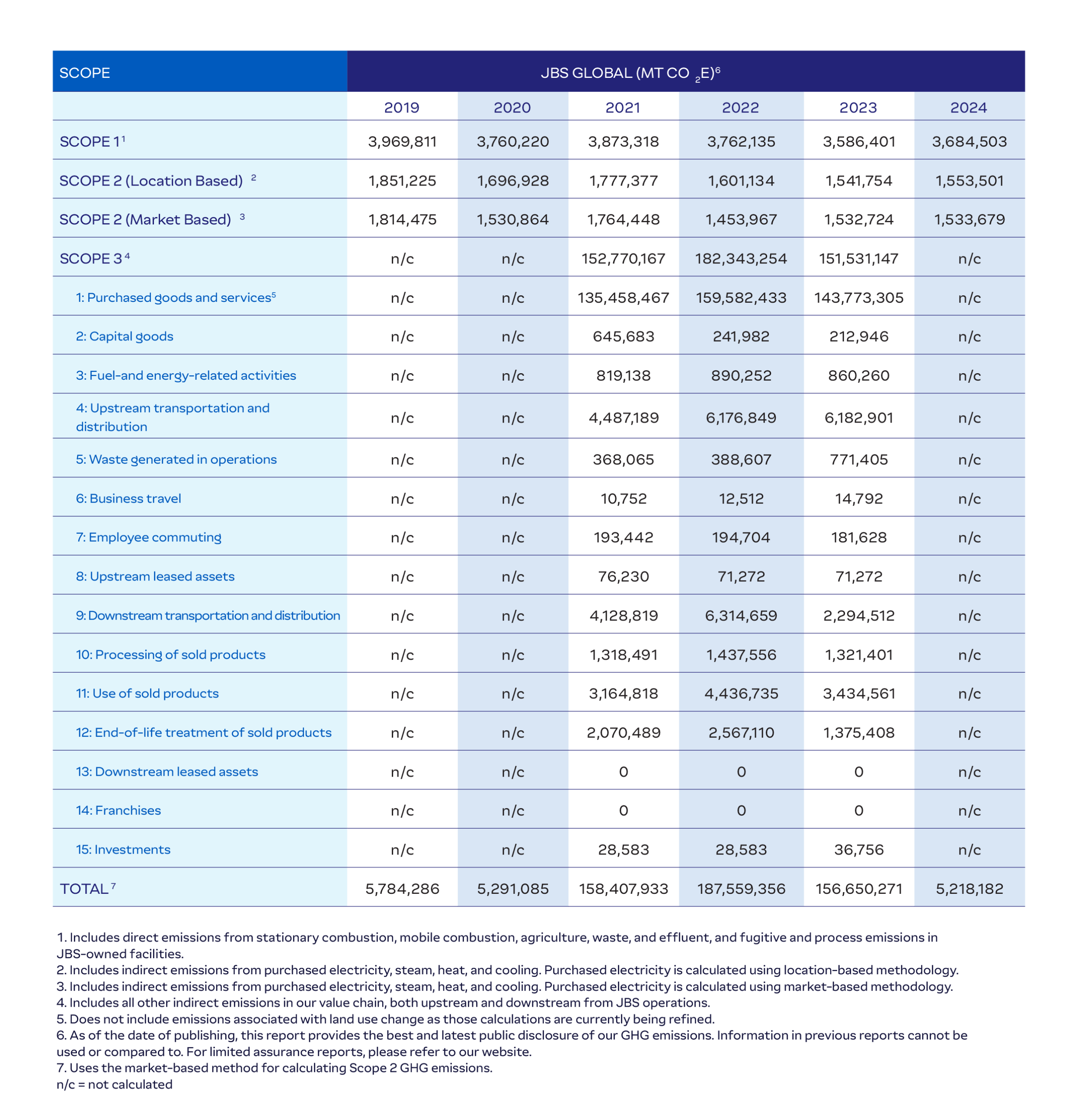
Our Emissions Profile
(SASB FB-MP-110a.1, FB-MP-110a.2)
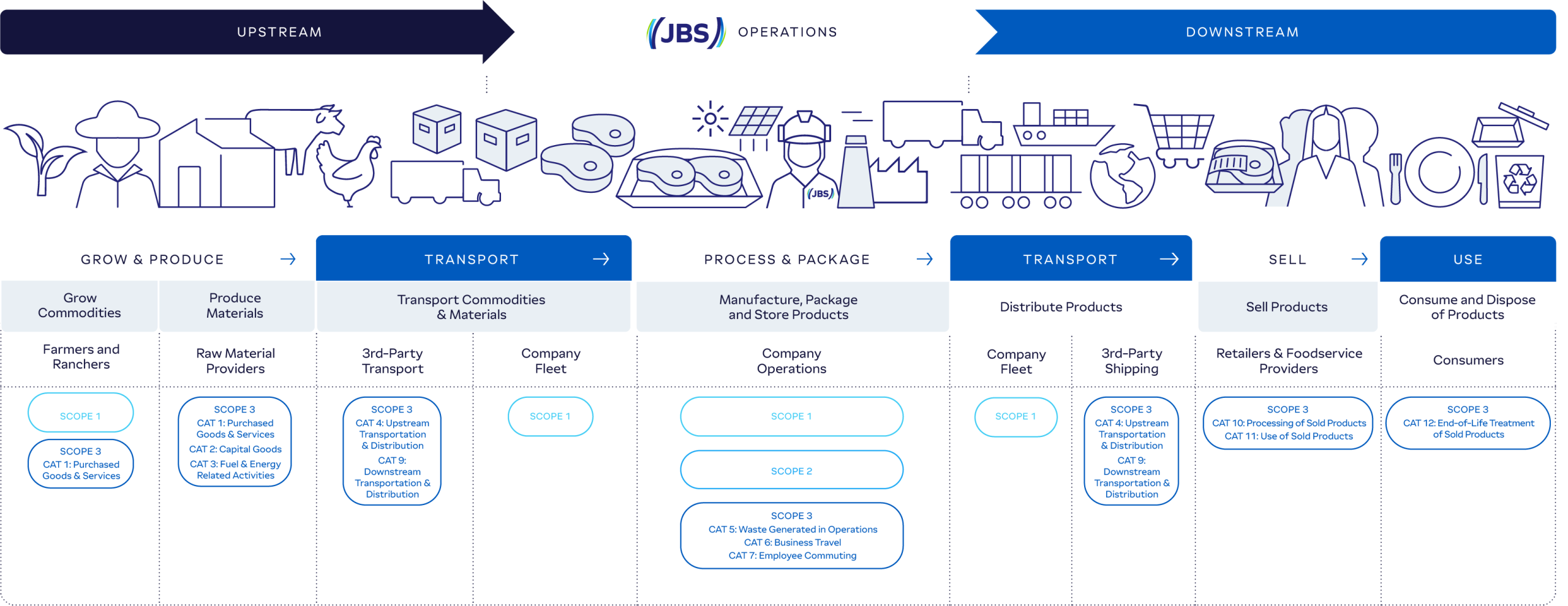
As with many companies in the food and agriculture sector, the majority of JBS’s GHG emissions footprint comes from indirect Scope 3 emissions. These emissions stem from activities outside of JBS’s control across its value chain, such as livestock and grain production, product distribution, and consumer use.
This presents a significant challenge because these Scope 3 emissions are not directly related to JBS’s operations and management. They are the result of thousands of individual farming operations that grow the agricultural commodities in our supply chain and millions of consumers cooking, refrigerating, and disposing of JBS products. Unlike Scope 1 and Scope 2 emissions, which are directly tied to our facilities and energy use, Scope 3 emissions require more collaboration and innovation across our value chain to achieve meaningful reductions.
JBS is working to address Scope 3 emissions by investing in partnerships, innovative technologies, and data-driven approaches to improve emissions measurement and management. By fostering collaboration across the value chain, we aim to create scalable solutions that enable us—and the broader agricultural industry—to transition toward a low-carbon future. Our efforts are focused on empowering farmers with sustainable practices, enhancing transparency through advanced data collection, and working closely with stakeholders to implement impactful climate strategies.
Climate Resiliency Beyond GHG Emissions
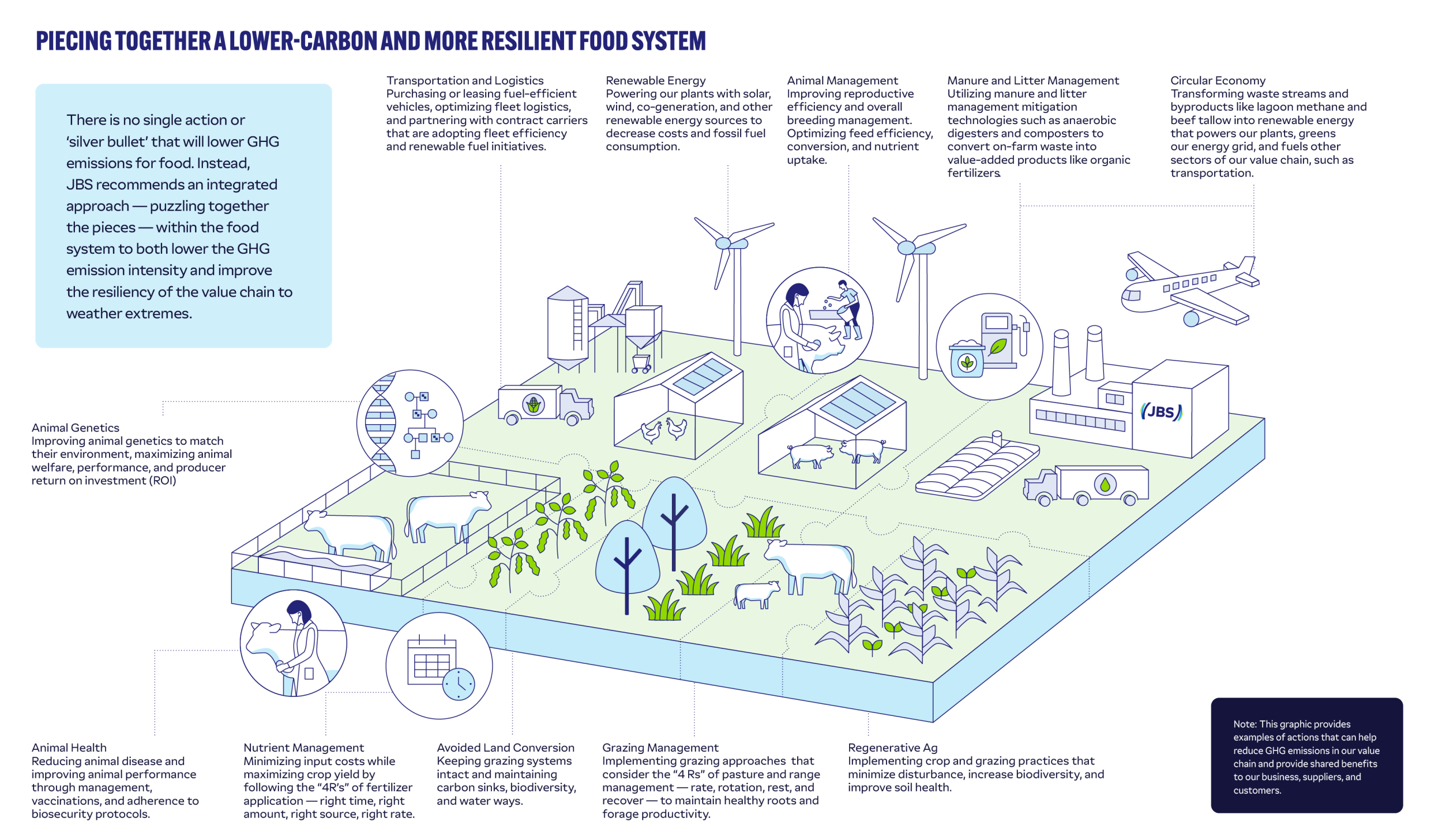
Building climate resiliency is essential for the long-term sustainability of our operations, supply chains, and the communities we serve. While reducing GHG emissions remains a priority, true resilience requires addressing broader climate-related risks such as droughts, floods, extreme weather events, and ecosystem shifts. These challenges can disrupt raw material availability, reduce productivity, and increase operational costs—directly impacting global food security.
To address these risks, we invest in initiatives that promote sustainable practices across our supply chain, focusing on key areas critical to climate adaptation: deforestation prevention, pasture management, soil health, water stewardship, animal health, and circular economy solutions.
Deforestation Prevention
Forest stability plays a vital role in influencing rainfall patterns, plant and animal biodiversity, water and soil quality, flood prevention, and economic vitality for smallholder farmers. To address the core drivers of deforestation risks in our Brazilian cattle supply, JBS has developed a multi-layered approach that includes:
Learn more about our strategies and actions to address deforestation in Land Management.
Pasture and Rangeland Management
Pasture and Rangeland Management support biodiversity, sequester carbon, and regulate water. By partnering with supply chain stakeholders, conservation organizations, and the livestock community, JBS aims to protect these ecosystems, ensuring their ecological and economic viability.
Soil Health and Water Stewardship
Soil health and water management play foundational roles in sustainable livestock and feed production. Healthy soils promote the growth of nutritious feed crops, which directly impact animal health and productivity. In addition, effective water management maintains clean and sufficient water supplies for livestock and crop irrigation, reducing environmental impact and improving regulatory compliance.
Animal Health and Performance
Climate strategies should be designed and deployed to instigate positive changes in animal production practices while also fostering long-term ecological and financial benefits for farmers and their land. Solutions must balance overall efficiency with high animal welfare and product quality standards.
Learn more about our animal care initiatives in Our Animals.
Circular Economy Solutions
Closed-loop systems for reusing and recycling waste materials and energy play an important role in the long-term viability of agricultural food production. Applying strategic, circular economy principles across our operations is an integral component of our business model, prompting us to create new businesses dedicated to this strategy. This integration supports economic growth by reducing operational costs and environmental footprints, ultimately fostering a more sustainable and resilient economy.
Learn more about our circular economy initiatives in Circular Economy and Reverse Logistics.
Case Studies:
The JBS LCA Working Group aims to:
- Improve scientific communication and collaboration across regions.
- Establish rigorous quality standards for LCA practices.
- Refine emissions baselines to better reflect JBS’s global supply chains.
- Support our customers in meeting their sustainability goals through credible, data-driven insights.
- Improve our business performance.
Currently, JBS is actively implementing LCA initiatives in Brazil, Europe, and Australia, with plans to expand globally.
