Our Environment
Circular Economy
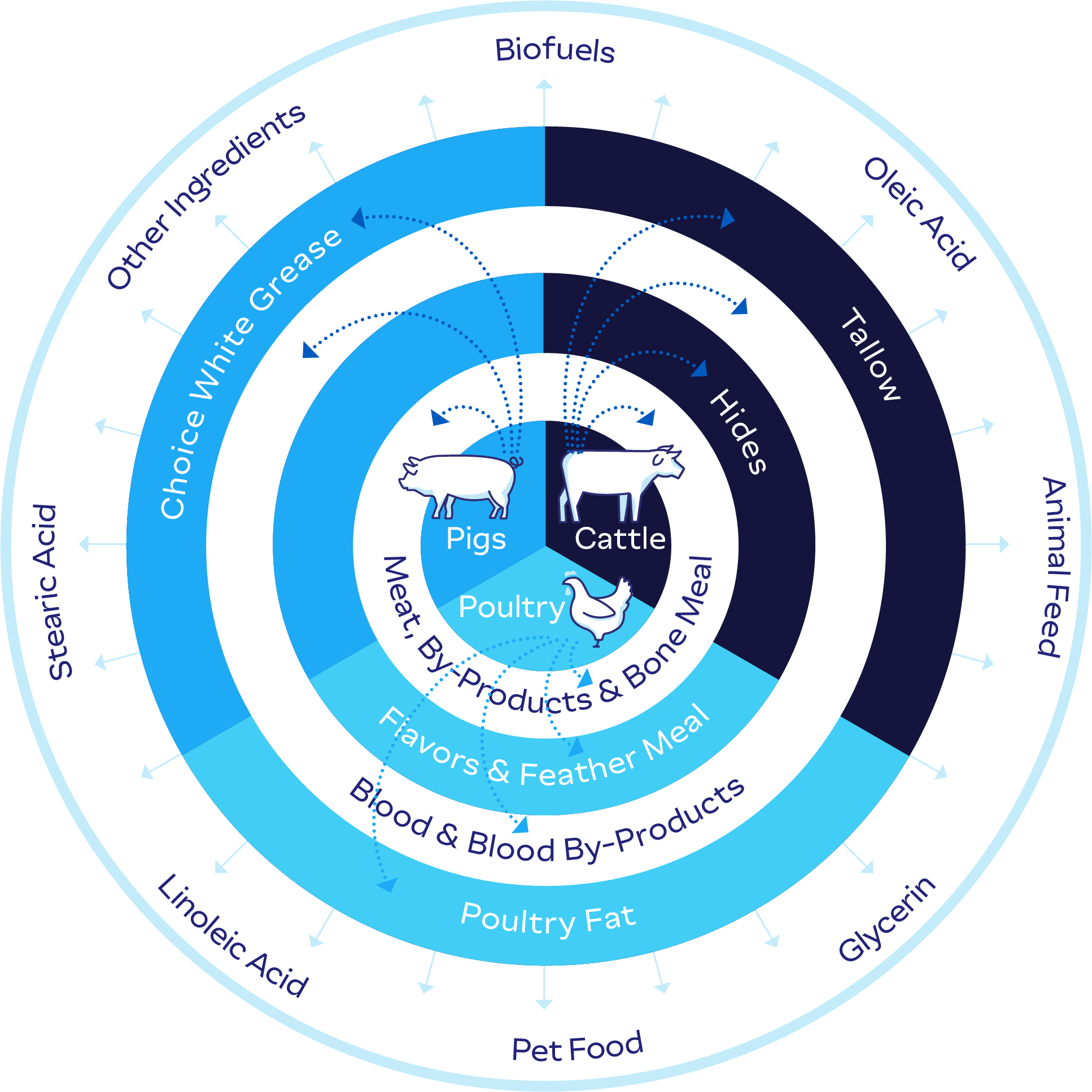
At JBS, we are working toward a future where resources are valued, and waste is minimized. We are actively integrating circular economy principles across our operations, moving beyond traditional linear models to embrace closed-loop systems that reduce, reuse, recover, and recycle materials and energy. This strategic shift is not just about minimizing disposal; it's about unlocking new business opportunities, driving disruptive innovation, and strengthening the long-term resilience of our operations. Circularity is now a growing component of our business model, influencing our long-term decisions and shaping a more sustainable future for JBS and the communities we call home.
For over two decades, we have been transforming what was once considered waste into valuable resources. Rendering — the process of repurposing byproducts that many consumers consider inedible and would otherwise go to waste — is an important but often overlooked component of food sustainability. Responsibly diverting these materials from landfills and other disposal methods helps reduce food waste, decrease GHG emissions, and return clean water to natural waterways. Many of these inedible byproducts are now the foundation for biodiesel, nutraceuticals, soaps, and animal feed. Used packaging and organic waste are also being repurposed into new packaging for our operations and fertilizers for agricultural use. These initiatives demonstrate our dedication to closing the loop and maximizing the value of every resource.
Advancing Circularity in Our Operations
Circularity is vital to the long-term viability of agricultural food production, which is why we have created dedicated business units in Brazil focused on advancing these principles. This investment not only supports economic growth by reducing operational costs, but also minimizes environmental footprints, ultimately fostering a more sustainable and resilient economy.
JBS Leather
JBS Leather is a global leader in leather production, operating across four continents and processing over 40,000 pieces of leather daily. Serving key industries such as automotive, furniture, and footwear, JBS Leather combines innovation, logistics, and value chain control to deliver high-quality leather products with enhanced consistency, ergonomics, and industrial automation. Through its advanced tanning processes, JBS Leather transforms animal hides—a byproduct of meat production—into versatile leather materials with applications across multiple industries. This process not only adds significant value but also repurposes raw materials that might otherwise be incinerated or sent to landfills. By utilizing animal hides generated in JBS's meat processing facilities, JBS Leather exemplifies a circular and responsible production model.
JBS Leather also generates raw materials for collagen and peptides, hygiene and cleaning products, and biodiesel, maximizing the value extracted from each hide. A strategic priority is the production of lime split leather, which focuses on generating casing scraps for collagen and gelatin production, reducing reliance on lowering meal.
JBS New Business
JBS New Business in Brazil represents a group of companies dedicated to converting traditional waste streams into innovative, value-added products. By applying closed-loop systems and circular economy principles, JBS New Business transforms byproducts and waste from animal protein processing into biodiesel, collagen, natural casings, fertilizers, nutraceuticals, personal care products, and more. These products are sold domestically in Brazil and exported to over 50 countries worldwide. Through innovation, efficiency, and sustainable practices, JBS New Business plays a vital role in advancing circularity across JBS operations. By unlocking the potential of materials traditionally considered waste, this business unit not only reduces environmental impact but also creates new revenue streams, contributing to the long-term viability of our operations and supporting a more sustainable global economy.



Our Solutions
Uboi: Digital service for live animal transport with trained drivers and 24/7 monitoring of animal welfare.
TRS: Fleet for transporting animals, leather, dry cargo, and goods, renewed every three years through Renova (our business dedicated to fleet renewal).
Co-Trade: Sells oils, fats, and chemical products, supporting efficient resource use across diverse markets.
H&B: Produces over one billion B2B soap units annually using beef tallow and other raw materials.
Casings: One of the world’s largest producer of natural casings for sausages and salamis, repurposing animal-based materials.
Biopower: Converts organic waste into biodiesel, producing 909 million liters annually and reducing GHG emissions.
Orygina: Supplies pharmaceutical and scientific industries with specialized animal-derived products.
Genu-in: Creates collagen peptides and gelatins for nutraceutical, food, and pharmaceutical applications.
Novapron: Global reference in the production of high-funcionality bovine collagen and ingredient solutions for the food industry.
Zempack: Manufactures over 1 billion aerosol and metallic packages annually, promoting reverse logistics.
Ambiental: Manages industrial waste for proper treatment and disposal of non-recyclable items.
Campo Forte: Produces fertilizers from organic waste to support sustainable agriculture.
No Carbon: Operates electric trucks for frozen and refrigerated product transport, reducing carbon emissions.
Bolstering Reverse Logistics
We strive to minimize landfill impacts and reduce the consumption of raw materials by encouraging the recycling and reuse of postconsumer packaging waste in our value chain. In addition to adhering to applicable local laws and regulations, such as the National Solid Waste Policy (Law No. 12,305 of August 2, 2010) in Brazil, we are actively developing projects in collaboration with Ambiental, a JBS New Business dedicated to transforming plastic waste into high-value-added products.
Food Waste
JBS also plays an active role in forums and initiatives aimed at reducing waste in global food production. We have improved our methods of disposing of and processing waste through several initiatives. In addition, we are minimizing overproduction and reducing inedible byproducts through leading inventory management systems. In 2024, Pilgrim’s Europe was as a signatory of the Food Waste Reduction Roadmap, reinforcing its dedication to tackling food waste.
Case Studies:
- Biogas Repurposing: Methane captured from the wastewater treatment plant (WWTP) is converted into biogas, which powers facility operations and reduces GHG emissions.
- Heat Recovery: Heat from condensates is captured and reused, improving energy efficiency.
- Sludge Utilization: Sludge from the WWTP is repurposed, further minimizing waste and enhancing resource recovery.
By closing the loop within its operations, the initiative significantly enhances energy efficiency at the plant while demonstrating the scalability of circular solutions for processing facilities worldwide. This model exemplifies how circular economy principles can drive both operational excellence and global sustainability in food production.
